Science: 2012: CBSE: [Delhi]: Set – I
To Access the full content, Please Purchase
-
Q1
Name the functional group present in each of the following organic compounds:-
(i) C2H5Cl (ii) C2H5OH
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
(i) The functional group present in C2H5Cl is Chloro
(-Cl).
(ii) The functional group present in C2H5OH is alcohol
(-OH).
-
Q2
What will be the colour of the sky when it is observed from a place in the absence of any atmosphere?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Dispersion of light does not take place when there is no atmosphere. Thus, the colour of the sky will be black when it is observed from a place where atmosphere is absent.
-
Q3
Which class of chemicals is linked to the decrease in the amount of ozone in the upper atmosphere of the earth?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) released from refrigerants and air-conditioner is linked to the decrease in the amount of ozone in the upper atmosphere of the earth.
-
Q4
Bacteria and fungi are called decomposers. Why?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Bacteria and fungi are called decomposers because they breakdown dead remains of plants and animals and decompose them into organic matter.
-
Q5
How can the valency of an element be determined if its electronic configuration is known? What will be the valency of an element of atomic number 9 (nine)?
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Valency of an element can be determined by its electronic configuration as follows:-
(i) If Valence electron ≤ 4
Then, Valency = Valence electrons
(ii) If Valence electron > 4
Valency = 8 –Valence electrons
Valency of an element of atomic number 9(nine):-
Electronic Configuration= 2, 7
Here, Valence electron=1
Valency= 8 – 7 = 1
-
Q6
An element ‘X’ has atomic number 13:
(a) Write its electron configuration
(b) State the group to which ‘X’ belongs
(c) Is ‘X’ a metal or a non-metal?
(d) Write the formula of its bromide.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Element X has atomic number 13
i. Electronic configuration= 2,8,3
ii. Valence electrons of X= 3
Group number= 3+10=13
Group to which X belongs is 13
iii. X is a non-metal
iv. Electronic configuration of Br is 2,8,18,7
Valency of Br= 1
Electronic Configuration of X is 2,8,3
Valency of X= 3
Element X= Aluminium(Al)
Formula of its bromide is AlBr3
-
Q7
State one genetically different feature between sperms and eggs of humans. What is its consequence?
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
The genetic difference between a sperm and an egg is that, a sperm contains either X or Y chromosome, while an egg always contains X chromosome. It is an essential factor for deciding the sex of a child as during fertilisation, an ovum fuses with a sperm carrying either an X chromosome or a Y chromosome. The zygote carrying XX chromosomes results in the formation of a girl child, while that carrying XY results in the formation of a boy child.
-
Q8
List two advantages of vegetative reproduction practiced in case of an orange plant.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Advantages of vegetative reproduction practiced in case of an orange plant are:
- It helps in the propagation of plants which have lost their ability to produce viable seeds.
- Plants produced are genetically similar to the parent plant and have similar characteristics.
-
Q9
List four properties of the image formed by a plane mirror.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Four properties of the image formed by a plane mirror are given below:
1. Image formed by plane mirror is virtual.
2. Image formed by plane mirror is erect and laterally inverted.
3. Size of both the object and its image is always same.
4. Image distance and object distance remains same.
-
Q10
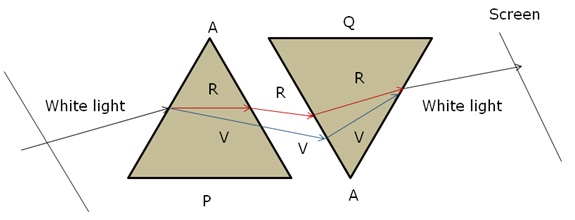
When we place a glass prism in the path of a narrow beam of white light, a spectrum is obtained. What happens when a second identical prism is placed in an inverted position with respect to the first prism? Draw a labeled ray diagram to illustrate it.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
When a second identical prism ‘Q’, is placed in an inverted position in front of the white light spectrum from a prism ‘P’, then again recombination of the spectrum produces white light.