Science 2015 CBSE [ All India ] Set I
To Access the full content, Please Purchase
-
Q1
Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of ethane.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
There are seven covalent bonds in a molecule of ethane.
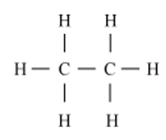
-
Q2
Name the life process of an organism that helps in the growth of its population.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Reproduction is the life process of an organism that helps in the growth of its population.
-
Q3
What will be the amount of energy available to the organisms of the 2nd trophic level of a food chain, if the energy available at the first trophic level is 10,000 joules?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
If 10,000 joules of energy is available at the first trophic level, 1000 joules of energy will be available at the 2nd trophic level of a food chain.
-
Q4
The absolute refractive indices of water and glass are 4/3 and 3/2 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is 2 x 108 m/s, calculate the speed of light in (i) vacuum, (ii) water
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
-
Q5
List two main causes of pollution of water of the river Ganga. State how pollution and contamination of river water prove harmful for the health of the people of neighbouring areas.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
The two main causes of the pollution of water of river Ganga are:
- Release of domestic wastes into the river Ganga
- Release of industrial effluents into the river Ganga
Pollution and contamination of river water is extremely harmful for the health of the people living in nearby areas as these people use the river water for domestic purposes. Drinking contaminated water causes many waterborne diseases like cholera, typhoid etc.
-
Q6
What is biodiversity? What will happen if biodiversity of an area is not preserved? Mention one effect of it.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Biodiversity is the variety of living organisms living in a particular area.
If biodiversity of an area is not preserved, species richness of that particular area will reduce and ecological balance will get disturbed, which in turn will reduce the number of feeding options for the consumers.
Thus in a long run, the population of consumers will get reduced.
-
Q7
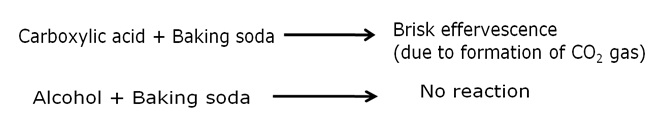
List two tests for experimentally distinguishing between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid and describe how these tests are performed.
Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
Two tests for experimentally distinguishing between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid are as follows:
a) Baeyer's reagent test: When alcohol is treated with few drops of a 5% alkaline potassium permanganate solution and kept in a hot water bath, the colour of potassium permanganate disappears. On the other hand, carboxylic acids do not show such reaction.
b) Sodium hydrogen carbonate test: Carboxylic acid on reaction with a solution of baking soda gives brisk effervescences due to evolution of carbon dioxide gas. When this gas is passed in lime-water, the later turns milky. Whereas, alcohol do not give effervescence with baking soda solution.
-
Q8
Draw the electron-dot structure for ethyne. A mixture of ethyne and oxygen is burnt for welding. In your opinion, why cannot we use a mixture of ethyne and air for this purpose?
Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
The electron-dot structure for ethyne, C2H2, is shown as:
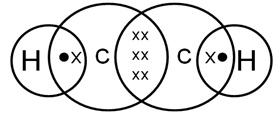
When ethyne is burnt with oxygen, it gives a clean flame with temperature of around 3,000 °C because of complete combustion. Hence, this mixture is used for welding purpose.
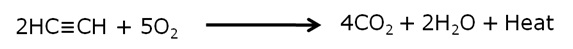
However, when ethyne is burnt with air, it gives a sooty flame. This is due to incomplete combustion caused by limited supply of oxygen obtained from air.
Thus, such a high temperature is not attained. Therefore, a mixture of ethyne and air is not used for welding purpose.
-
Q9
Two elements 'P' and 'Q' belong to the same period of the modern periodic table and are in Group-1 and Group-2 respectively. Compare their following characteristics in tabular form :
(a) The number of electrons in their atoms
(b) The sizes of their atoms
(c) Their metallic characters
(d) Their tendencies to lose electrons
(e) The formula of their oxides
(f) The formula of their chlorides
Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
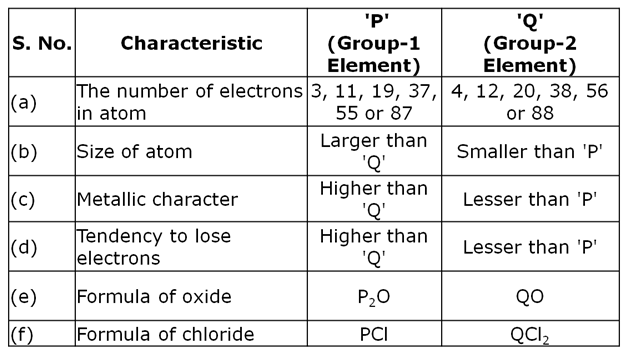
-
Q10
Taking the example of an element of atomic number 16, explain how the electronic configuration of the atom of an element relates to its position in the modern periodic table and how valency of an element is calculated on the basis of its atomic number.
Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged in 18 vertical columns called groups and 7 horizontal rows called periods. Elements with similar electronic configurations are placed in the same column. Number of valence electrons decides the group of the element and number of shells decides the period of the element.
The valency of an element is determined in the following manner:
a) If the number of electrons in the valence shell is less than 3, then the same number of electrons will represent the valency of that element.
b) If the number of valence electrons is either equal to or greater than 4, then that number is subtracted from 8 to obtain the valency of that element.An element of atomic number 16 has the electronic configuration: 2, 8, 6
It has six valence electrons and three shells. So, its valency is two.
It is positioned in Period 3 and Group 16.



