Science 2015 CBSE [All India] Set III
To Access the full content, Please Purchase
-
Q1
Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of butane, C4H10.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
There are thirteen covalent bonds in a molecule of butane.
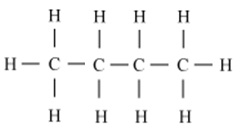
-
Q2
Name two simple organisms having the ability of regeneration.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Hydra and Planaria
-
Q3
Which of the following are always at the second trophic level of food chains?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Herbivorous
-
Q4
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror and show the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
-
Q5
Why is sustainable management of natural resources necessary? Out of the two - reuse and recycle - which, in your opinion, is better to practice? Give reason.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Sustainable management of natural resources is necessary to preserve them for the future generations and also to control environment pollution.
Reusing is a better option than recycling because recycling requires lot of energy and money. Reuse of products also creates less air and water pollution than recycling.
-
Q6
What is meant by bio-diversity? List two advantages of conserving forests and wild life.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Biodiversity is the degree of variety of living organisms within the different ecosystems.
The two advantages of conserving forests and wildlife are:
i. They provide us various valuable things that are required for our survival.
ii. They add natural beauty to the environment.
-
Q7
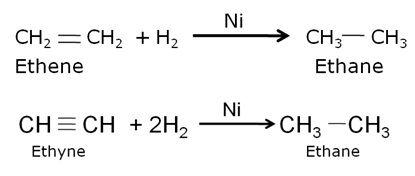
Write the name and general formula of a chain of hydrocarbons in which an addition reaction with hydrogen is possible. State the essential condition for an addition reaction. Stating this condition, write a chemical equation giving the name of the reactant and the product of the reaction.
Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
The hydrocarbons in which addition reaction with hydrogen is possible are alkenes and alkynes. The general formula for alkenes is CnH2n and for alkynes is CnH2n–2
Conditions for addition reaction are:
i) An unsaturated compound
ii) A suitable catalyst.
iii) A reactant molecule which should be added to the unsaturated hydrocarbon.
-
Q8
List two tests for experimentally distinguishing between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid and describe how these tests are performed.
Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
Two tests for experimentally distinguishing between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid are as follows:
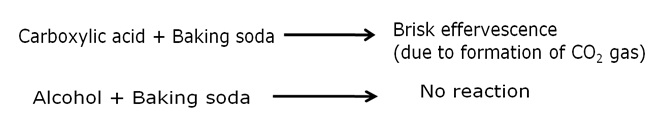
a) Baeyer's reagent test: When alcohol is treated with few drops of a 5% alkaline potassium permanganate solution and kept in a hot water bath, the colour of potassium permanganate disappears. On the other hand, carboxylic acids do not show such reaction.
b) Sodium hydrogen carbonate test: Carboxylic acid on reaction with a solution of baking soda gives brisk effervescences due to evolution of carbon dioxide gas. When this gas is passed in lime-water, the later turns milky. Whereas, alcohol do not give effervescence with baking soda solution.
-
Q9
Given below are some elements of the modern periodic table. Atomic number of the element is given in the parentheses:
A(4), B(9), C(14), D(19), E(20)
(a) Select the element that has one electron in the outermost shell, also write the electronic configuration of the element.
(b) Which two elements amongst these belong to the same group? Give reason for your answer.
(c) Which two elements amongst these belong to the same period? Which one of the two has bigger atomic radius?
Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
(a) D(19) has one electron in the outermost shell. Its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 8, 1.
(b) Elements A(4) and E(20) belong to same group.. Both the elements have 2 valence electrons in the outermost shell.
A(4): 2, 2
E(20): 2, 8, 8, 2
(c) A(4) and B(9) belong to second period elements D(19) and E(20) belong to fourth period of the modern periodic table. Atomic radius decreases on moving left to right along the period. Therefore, atomic radius of A(4) is bigger than B(9) and atomic radius of D(19) is bigger than E(20).
-
Q10
Taking the example of an element of atomic number 16, explain how the electronic configuration of the atom of an element relates to its position in the modern periodic table and how valency of an element is calculated on the basis of its atomic number.
Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged in 18 vertical columns called groups and 7 horizontal rows called periods. Elements with similar electronic configurations are placed in the same column. Number of valence electrons decides the group of the element and number of shells decides the period of the element.
The valency of an element is determined in the following manner:
a) If the number of electrons in the valence shell is less than 3, then the same number of electrons will represent the valency of that element.
b) If the number of valence electrons is either equal to or greater than 4, then that number is subtracted from 8 to obtain the valency of that element.An element of atomic number 16 has the electronic configuration: 2, 8, 6
It has six valence electrons and three shells. So, its valency is two.
It is positioned in Period 3 and Group 16.



