Science:2015:CBSE:[Delhi]:Set-II
To Access the full content, Please Purchase
-
Q1
Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n+ 2.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
CnH2n+2 is the general formula for the alkane series. The second member of the alkane family is ethane having formula C2H6.
-
Q2
What is the magnification of the images formed by plane mirrors and why?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:

-
Q3
What is meant by power of a lens?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Power of lens is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length(in metres).
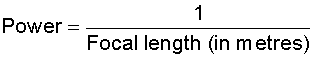
-
Q4
Write two differences between binary fission and multiple fission in tabular form.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Binary Fission
Multiple Fission
In binary fission two daughter cells are produced
In multiple fission more than two daughter cells are produced
The nuclear division is followed by cytoplasmic division
The nuclear division is not followed by cytoplasmic division
-
Q5
a. Why do we need to manage our resources carefully?
b. Why management of natural resources requires a long term perspective?Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
a. We need to manage our resources carefully because the human population is increasing at tremendous rate due to improvement in health care. As a result the demand for all the resources is increasing at exponential rate which are very limited in nature.
b. The management of natural resources requires a long term perspective because the demand of these natural resources is increasing exponentially and in order to meet the need and demand of next generations, the natural resources must be used carefully. -
Q6
List four measures that can be taken to conserve forests.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Four measures that can be taken to conserve forests are:
1. Indiscriminate cutting of trees or deforestation should be prohibited.
2. Forest fire should be controlled.
3. Alternative sources of energy, like biogas should be used instead of fuel wood.
4. Reforestation of the deforested area should be undertaken. -
Q7
Na, Mg and Al are the elements of the same period of Modern Periodic Table having, one, two and three valence electrons respectively. Which of these elements (i) has the largest atomic radius, (ii) is least reactive? Justify your answer stating reason for each case.
Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
(i) When we move from left to right across a period in the periodic table, atomic radius decreases due to increase in nuclear charge which pulls the outermost electron closer to the nucleus. Therefore, sodium has the largest atomic radius among these elements.
(ii) Among the given elements, aluminium is the least reactive element because when we move from left to right across a period in the periodic table, the reactivity decreases due to increased nuclear charge which makes the loss of outermost electron by the element difficult. -
Q8
From the following elements:
4Be; 9F; 19K; 20Ca
(i) Select the element having one electron in the outermost shell.
(ii) Two elements of the same group.(iii)Write the formula of and mention the nature of the compound formed by the union of 19K and element X (2, 8, 7).
Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
(i) Among the given elements, 19K has one electron in the outermost shell as its electronic configuration is 2, 8, 8, 1.
(ii) The elements 4Be and 20Ca belong to the same group, i.e., Group 2 as both elements have two electrons each in their outermost shells.
Electronic configuration of 4Be = 2, 2.
Electronic configuration of 20Ca = 2, 8, 8, 2.(iii) The atomic number of element X = 17
Electronic configuration of element X = 2, 8, 7.
Number of valence electrons in X = 7
Valency of X = 8 − 7 = 1
Similarly, Atomic number of element K = 19Electronic configuration of K is 2, 8, 8, 1.
Number of valence electron in K = 1
Valency of K = 1
Therefore, on combining the elements K and X, we get the formula of compound as KX.The compound KX is of ionic nature.
-
Q9
What is meant by isomers? Draw the structures of two isomers of butane, C4H10. Explain why we cannot have isomers of first three members of alkane series.
Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
The compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural formulae are known as isomers.
The two structural isomers of butane are:
Lower alkanes i.e. methane, ethane and propane do not exhibit isomerism as they are too short to have branched structures required to show structural isomerism. -
Q10
What is the difference between the molecules of soaps and detergents, chemically? Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
Soap molecules are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids or higher fatty acids. They form scum upon reaction with calcium and magnesium ions present in hard water.
Detergent molecules are ammonium or sulphonate salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. They do not form insoluble precipitates with calcium and magnesium ions.
Cleansing action of soaps: The dirt or oil droplet present on clothes is organic in nature and is insoluble in water. Hence, it cannot be removed by only washing with water. When soap is dissolved in water, its hydrophobic ends attach themselves to the dirt. Then, the molecules of soap arrange themselves in micelle formation and trap the dirt at the centre of the cluster. These micelles remain suspended in the water. When cloth is rinsed in water, the dirt particles are easily washed away.



