Accountancy : Company Accounts and Analysis of Financial Statements 2004 CBSE [ Delhi ] Set I
To Access the full content, Please Purchase
-
Q1
List any four contents of a partnership deed. Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
A partnership deed generally contains the following particulars: (i) Names and addresses of the firm and the partners. (ii) Duration of the partnership (iii) Capital employed by different partners (iv) Ratio in which profits are to be shared. -
Q2
Distinguish between “Reserve Capital” and “Capital Reserve”. Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Distinction between Reserve Capital and Capital Reserve Points of distinction Reserve Capital Capital Reserve 1) Nature Reserve capital is a portion of uncalled capital Capital reserve is the accumulation of profits of capital nature. 2) Disclosure Reserve capital is not shown in the balance sheet of the company Capital reserve is shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet under the heading “reserves and surplus” 3) Time of receipt Reserve capital is a portion of uncalled capital and receivable only at the time of winding-up Capital reserve is the amount already received by the company 4) Application Reserve capital is a portion of uncalled capital and receivable only at the time of winding-up Capital reserve may be applied ant time to write off the capital losses. 5) Option It is not mandatory to create reserve capital It is mandatory to create capital reserve in case of capital profits. -
Q3
What is meant by “ Private Placement of Shares"? Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Section 81(1A) of the companies Act allows a public company to issue shares through the private placement route. Private placement of shares means issue of shares to a selected group of persons. Such an issue is subject to SEBI guidelines relating to preferential allotment. Such an issue requires a special resolution or a general resolution and consent of the central government to this effect. -
Q4
State the meaning of “Debentures issued as Collateral Security” Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Collateral security means an additional security or subsidiary security. Sometimes a company issues debentures as collateral security against loan taken from banks or other agencies. Collateral security is to be realised only when the principal security fails to pay the amount of loan. On the repayment of loan, collateral security reverts to the company. The liability of the company is for the amount of loan and not for the face value of debentures issued. In case, the company makes a default in the repayment of the loan, the loan creditor will become a debenture holder. No interest is payable on the debenture issued as a collateral security. -
Q5
How are the various activities classified according to As-3(Revised) while Preparing the cash flow statement ? Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
The various activities classified according to As-3(Revised) while preparing the cash flow statement are:
(1)Operating activities (2) Investing activities (3) Financing activities. -
Q6
Give two examples each of cash flow from investing activities and cash flows from financing activities. Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Examples from cash flows from investing activities- 1) sale of investments 2) Purchase of machinery Examples from cash flow from financing activities- 1) Cash received from issue of shares 2) Payment of dividend -
Q7
The partners of a firm distributed the profits for the year ended 31st March, 2003 , Rs.90,000 in the ratio of 3:2:1 without providing for the following adjustments: 1) A and B were entitled to salary of 1,500 each per annum. 2) B was entitled to a commission of Rs.4,500. 3) B and C had guaranteed a minimum profit of Rs.35,000 p.a to A 4) Profits were to be shared in the ratio of 3:3:2. Pass necessary journal entry for the above adjustments in the books of the firm. Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
Statements showing adjustment to be made in capital accounts. Particulars A B C Firm Profit already distributed now debited Salary Commission Profit guaranteed to A Profit distributed between B and C in the ratio of 3:2 Adjustment required Net Effect Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. Dr. Cr. 45,000 -- -- -- -- -- 1,500 -- 35,000 -- 30,000 -- -- -- -- -- 1,500 4,500 -- 28,500 15,000 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 19,000 -- 3,000 4,500 35,000 47,500 90,000 -- -- -- -- 45,000 -- 36,500 8,500 30,000 4,500 34,500 -- 15,000 4,000 19,000 -- 90,000 -- 90,000 -- 45,000 45,000 34,500 34,500 19,000 19,000 90,000 90,000 8,500 4,500 4,000 Journal Date Particulars L.F Dr. Cr. A’s Capital A/c Dr. To B’s Capital A/c To C’s Capital A/c (adjustment entry recorded due to several adjustments omitted earlier) 8,500 4,500 4,000 -
Q8
Pass necessary journal entries in the books of the company in following cases for redemption of 1,000, 12% Debentures of Rs.10 each issued at par: a) Debentures redeemed at par by conversion into 12% preference shares of Rs.100 each. b) Debentures redeemed at a premium of 10% by conversion into Equity shares issued at par
c)Debentures redeemed at a premium of 10% by conversion Equity shares issued at a premium of 25% Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
Journal Date Particulars L.F Dr. Cr. a) 12% Debentures A/c To 12% Preference share capital A/c (Redemption of debentures by conversion into preference shares issued at par) 10,000 10,000 b) 12% Debentures a/c Dr. Premium on Redm. of deb. a/c To equity share capital A/c (redemption of debentures at premium by conversion into equity shares) 10,000 1,000 11,000 c) 12% Debentures A/c Dr . Prem. On redm. Of Deb. a/c To Equity share capital a/c To Security premium a/c (Redemption of debentures at premium by conversion into equity shares issued at premium) 10,000 1,000 8,800 2,200 Working Notes: a) No of preference shares to be issued = amount due to debenture holders / agreed value of shares = 10,000 / 10 = 100 preference shares. b) No. of equity shares to be issued = amount due to debenture holders / agreed value of share = 10,000 + 1,000 / 10 = 1,100 shares c) No. of equity shares to be issued = Amount due to debenture holders / agreed value of share = 10,000 + 1,000 / 10+2.5 = 11,000 / 12.5 = 880 shares. -
Q9
Give the format of balance sheet of a company (main headings only), as per requirements of schedule VI of the companies Act. 1956. Marks:3View AnswerAnswer:
Balance sheet of ------ As at ---- Figures for the previous year Liabilities Figures for the current year Figure for the previous year Assets Figures for current years 1.Share capital 2. Reserve and surplus 3. Secured loan 4. Unsecured loan 5. Current liabilities and prov. 1.Fixed assets 2. Investments 3. Current assets , loan and advances 4. Miscellaneous expenditure 5.Profit and loss a/c -
Q10
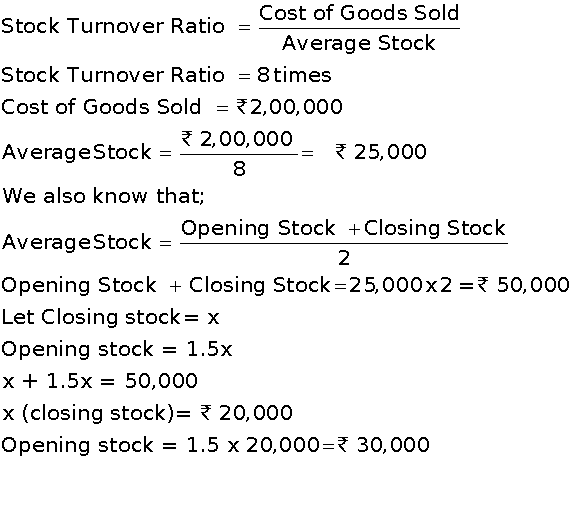
Rs.2,00,000 is the cost of goods sold, inventory turnover 8 times; Stock at the beginning is 1.5 times of the closing stock. Calculate the values of opening and closing stocks. Marks:3View AnswerAnswer: