Biology:2012:CBSE:[All India]:Set-III
To Access the full content, Please Purchase
-
Q1
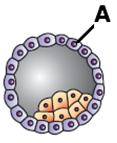
Identify the figure given below and the part labelled “A”.
 Marks:1View Answer
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
The given figure is of Blastocyst and the part labelled “A” is 'Trophoblast (the outer layer)'.
-
Q2
How do interferons protect us?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Interferons are anti-viral proteins (released by virus infected cells) that protect our non-infected cells from further viral infection.
-
Q3
Name the interaction between a whale and the barnacles growing on its back.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Commensalism is the interaction between a whale and the barnacles growing on its back.
-
Q4
In a dihybrid cross, when would the proportion of parental gene combinations be much higher than non-parental types, as experimentally shown by Morgan and his group?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
In a dihybrid cross, when the two genes are located on the same chromosome then the proportion of parental gene combinations be much higher than non-parental types, it was experimentally shown by Morgan and his group in process of linkage and recombination.
-
Q5
Why is banana considered a good example of parthenocarpy?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Parthenocarpic fruits are either seedless or contain non-viable seeds as in banana fruits. Hence, banana is considered a good example of parthenocarpy.
-
Q6
Why is it desirable to use unleaded petrol in vehicles fitted with catalytic converters?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Vehicles fitted with catalytic converters should use unleaded petrol because lead in the petrol inactivates the metal catalyst present in the converter.
-
Q7
Comment on the similarity between the wing of a cockroach and the wing of a bird. What do you infer from the above with reference to evolution?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Wing of a cockroach and wing of a bird are analogous organs as their origin is not the same but they perform similar functions. From the above example one can infer the evolutionary relationship between organisms.
-
Q8
Mention the role of cyanobacteria as a biofertiliser.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Cyanobacteria such as Anabaena and Nostoc, fix atmospheric nitrogen. They serve as important bio-fertilisers especially in paddy fields.
-
Q9
Name the cells that act as HIV factory in humans when infected by HIV. Explain the events that occur in the infected cell.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
Macrophages act as HIV factory in humans when infected by HIV.
The events that occur in the infected cells are:
a) After entering into human body, HIV enters into macrophages (human cell)
b) In macrophage, RNA genome of virus replicates into viral DNA by the process of reverse transcription
c) Viral DNA is incorporated into host cell DNA
d) Viral DNA directs infected cell to produce viral particles.
e) After assembling of viral particles the virus ruptures the infected cell.
f) Simultaneously, new HIV particles infect helper T-lymphocytes by replicating and producing viral progeny.
g) Viral progeny released in blood attacks other helper T-cells and this repeated process leads to progressive decrease in the number of helper T-lymphocytes -
Q10
Name and explain the two types of immune responses in humans.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
The two types of immune responses in humans are:
i) Humoral immune response- It is a primary immune response mediated by B-lymphocytes. B-lymphocytes originate and mature in bone marrow and later migrate to lymphoid tissue throughout the body. Production of antibodies by B-lymphocytes is stimulated by helper T cells and suppressed by suppressor T cells. Some B cells are changed into plasma cells, which produce antibodies but some get transformed into memory cells which recognise the same antigen when introduced subsequently. The antibodies are found in blood hence such type of response is also called antibody mediated immunity (AMI).
ii) Cell mediated immune response (CMI) - It is regulated by T-lymphocytes. It is also known as cell mediated immunity. T-lymphocytes originate in bone marrow and migrate to thymus gland for maturation and later migrate to lymphoid tissue present throughout the body. CMI is responsible for graft rejection in transplanting organs. An activated cytotoxic T cell (sub group of T cells) is specific to infected target cell and kills it before the life cycle of pathogen completes. Cancer cells are also killed by cytotoxic T-cells. CMI protects the body against, fungi, bacteria and many viruses.



