Chemistry:2019:CBSE:[Delhi]: Set-III
To Access the full content, Please Purchase
-
Q1
Arrange the following in decreasing order of solubility in water.
(CH3)3N, CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
The decreasing order of solubility in water is
CH3NH2 > (CH3)2NH > (CH3)3N
The more extensive the hydrogen bonding, higher is the solubility.
CH3NH2: Lower amines are soluble in water as they are capable to form hydrogen bonds with water. CH3NH2 contains two hydrogen atoms attached to the nitrogen and undergoes hydrogen bonding easily.
(CH3)2NH: (CH3)2NH contains only one hydrogen atom attached to the nitrogen. Thus, solubility of (CH3)2NH in water is less than that of CH3NH2.
(CH3)3N: Tertiary amines do not have hydrogen atom attached to the nitrogen and therefore, cannot form hydrogen bonds with themselves. The solubility of amines decreases with increase in molar mass of amines.
-
Q2
What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by ZnS and why?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Frenkel defect is shown by ZnS due to the large difference in the size of ions, i.e., Zn2+ and S2–.
-
Q3
Write one stereochemical difference between SN1 and SN2 reactions.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Formation of carbocation in the transition state of SN1 reaction leads to the formation of racemic mixture whereas in SN2 reaction, carbocation generation and substitution take place in single step that leads to inversion in configuration of the product.
-
Q4
Why are medicines more effective in colloidal state?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Medicines are more effective in colloidal state because they have large surface area in colloidal form. Therefore, they are easily assimilated and absorbed by the body tissues.
-
Q5
What is difference between an emulsion and a gel?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
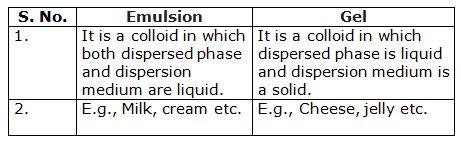
-
Q6
What is the basic structural difference between glucose and fructose?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Glucose has an aldehyde group and fructose has ketone group. Glucose is an aldohexose while, ketone is a ketohexose.
-
Q7
Write the products obtained after hydrolysis of lactose.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
The products obtained after hydrolysis of lactose are β-D-Glucose and β-D-Galactose.
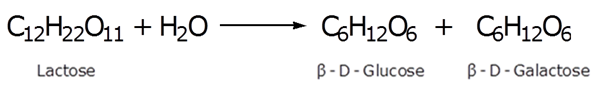
-
Q8
When MnO2 is fused with KOH in the presence of KNO3 as an oxidizing agent, it gives a dark green compound (A). Compound (A) disproportionates in acidic solution to give purple compound (B). An alkaline solution of compound (B) oxidises KI to compound (C) whereas an acidified solution of compound (B) oxidises KI to (D). Identify (A), (B), (C) and (D).
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:

Hence, A = Potassium manganate (K2MnO4)
B = Potassium permanganate (KMnO4)
C = Potassium iodate (KIO3)
D = Iodine (I2)
-
Q9
State Henry’s law and write its two applications.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
According to Henry’s law " at a constant temperature, the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas present above the surface of liquid or solution."
Applications of Henry’s law:
(i) To increase the solubility of carbon dioxide in soft drinks, the bottle is sealed under high pressure.
(ii) To minimise the painful effects of scuba divers during decompression, oxygen diluted with less soluble helium gas is used by sea divers.
-
Q10
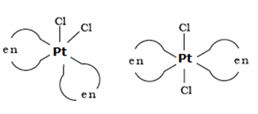
Write IUPAC name of the complex [Pt(en)2Cl2]. Draw structures of geometrical isomers for this complex.
Marks:2View AnswerAnswer:
IUPAC name of the complex [Pt(en)2Cl2] is bis(ethan-1,2-diamine)dichloridoplatinum (II).
Geometrical isomers for this complex are as follows