Economics : 2014 : CBSE : [Delhi] : Set – I
To Access the full content, Please Purchase
-
Q1
Unemployment is reduced due to the measures taken by the government. State its economic value in the context of production possibilities frontier.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
If unemployment is reduced, it would increase production of output and income leading to rightward shift in production possibility frontier. It indicates better utilization of resources as the economy can produce more goods and services with the increased labour.
-
Q2
Define budget set.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
A budget set is defined as the attainable combinations of two goods, given the prices of the goods and income of the consumer.
-
Q3
What is meant by revenue in microeconomics?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Revenue refers to the money receipts of a firm from the sales of its output.
-
Q4
Give meaning of 'returns to a factor.'
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Returns to a factor means the change in the physical output of a good when the quantity of one variable factor of production is increased keeping all the other factors constant. It is a short term phenomenon.
-
Q5
What is perfect oligopoly?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Perfect oligopoly refers to the oligopoly market situation in which the firms produce homogeneous products.
-
Q6
What are demand deposits?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Demand deposits refer to those deposits of commercial banks which can be withdrawn from the bank on demand or by writing the check anytime.
-
Q7
What is involuntary unemployment?
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Involuntary unemployment refers to the situation in which a worker in willing to work at the prevailing wage rate but does not get any work.
-
Q8
Define marginal propensity to consume.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Marginal propensity to consume is defined as the ratio of change in consumption to the change in the income.
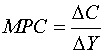
-
Q9
Define government budget.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
A government budget is an annual statement showing the estimated receipts and expenditure of the government during a financial year.
-
Q10
Give meaning of balance of trade.
Marks:1View AnswerAnswer:
Balance of trade refers to the difference between the value of imports and exports of the physical or visible goods.



